new promising os trend: Summit’s Phase 3 global data

new promising os trend: Summit’s Phase 3 global data
The oncology world is buzzing with excitement following the release of groundbreaking data from Summit Therapeutics. The company announced that its Phase 3 HARMONi-3 study met its primary endpoint, showcasing a statistically significant improvement in Overall Survival (OS). This development represents a new promising OS trend for patients with a specific, hard-to-treat form of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), potentially setting a new standard of care for a global patient population.
The study centers on ivonescimab, a novel bispecific antibody, combined with chemotherapy. The results are particularly impactful for patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated, locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC who have progressed after treatment with a third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). Let’s dive into what this data means for patients, clinicians, and the future of cancer therapy.
Article Contents
The Summit Study: A Deep Dive into HARMONi-3
The HARMONi-3 trial is a global, multicenter, double-blinded Phase 3 study that has captured the attention of researchers worldwide. Its primary goal was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ivonescimab plus chemotherapy compared to a placebo plus chemotherapy in a very specific patient group: those with advanced EGFR-mutated non-squamous NSCLC whose disease had worsened despite prior treatment with powerful drugs like osimertinib.
This patient population represents a significant unmet medical need. Once their cancer progresses past third-generation TKIs, treatment options become limited and often yield poor outcomes. The HARMONi-3 study, therefore, sought to answer a critical question: could this novel immunotherapy combination extend the lives of these patients?
The primary endpoint was Overall Survival (OS), considered the gold standard in oncology trials because it directly measures whether a treatment helps patients live longer. The study’s design was robust, ensuring that the results would be both credible and impactful. The positive outcome indicates that the trial successfully demonstrated a clear survival benefit for the group receiving ivonescimab.
Decoding the Data: Why This is a New Promising OS Trend
The headline result is clear: ivonescimab in combination with chemotherapy led to a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in Overall Survival. While specific figures from the full dataset are pending presentation at an upcoming major medical conference, the announcement confirms that the therapy arm substantially outperformed the placebo arm. This isn’t just an incremental improvement; it marks a significant leap forward and establishes a new benchmark for what is possible in this treatment setting.
This finding is more than a single success; it signals a new promising OS trend in oncology. For years, the focus has been on targeted therapies and single-pathway immunotherapies. The success of ivonescimab, a bispecific antibody, suggests that simultaneously targeting multiple cancer-driving pathways can unlock a new level of efficacy. It validates the strategy of combining checkpoint inhibition (PD-1) with anti-angiogenesis (VEGF) in a single molecule, especially after resistance to other treatments has developed.
Experts believe this could pave the way for similar dual-action therapies across different cancer types. The ability to overcome resistance and extend survival in such a heavily pre-treated population is a powerful proof of concept. For more information on existing lung cancer treatments, you can explore our guide on treatment options for NSCLC.
What is Ivonescimab and How Does It Work?
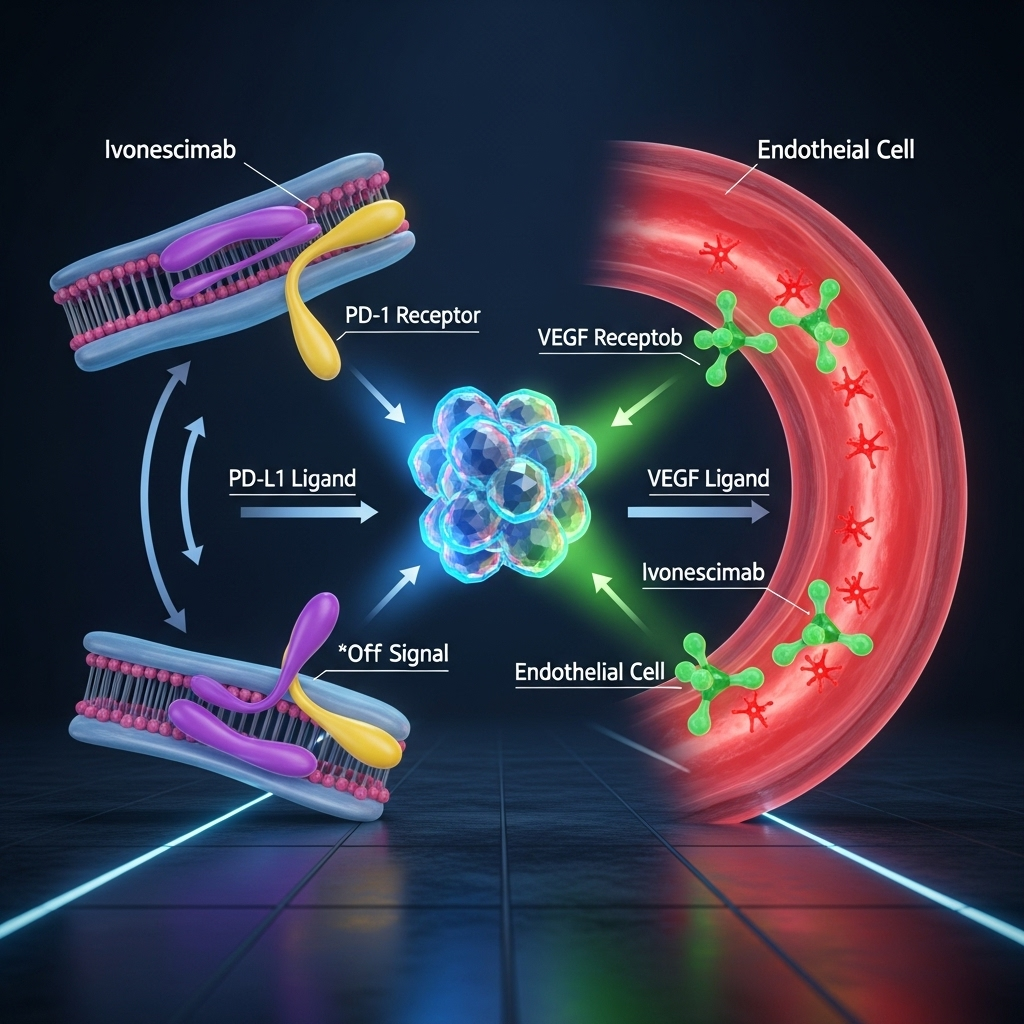
Ivonescimab (also known as AK112) is the star of the show. It’s not a standard chemotherapy drug or a typical immunotherapy agent. It is a novel, first-in-class bispecific antibody. This means it’s engineered to bind to two different targets simultaneously: PD-1 and VEGF.
- PD-1 (Programmed cell death protein 1): This is a well-known checkpoint on immune cells. Cancers often exploit PD-1 to hide from the immune system. By blocking PD-1, ivonescimab “takes the brakes off” the immune system, allowing it to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- VEGF (Vascular endothelial growth factor): This protein is crucial for angiogenesis—the process tumors use to grow their own blood vessels to get nutrients. By blocking VEGF, ivonescimab essentially starves the tumor and cuts off its supply lines.
The innovation lies in combining these two powerful mechanisms into one drug. This dual-pronged attack is designed to be more effective than administering two separate drugs targeting each pathway. The antibody is engineered to have a stronger binding affinity in the tumor microenvironment, potentially localizing its powerful effects where they are needed most while minimizing side effects elsewhere in the body. This elegant design is at the heart of why we are seeing such a new promising OS trend emerge from this research.
Implications for Patients and the Future of Lung Cancer Treatment
For patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC who have exhausted other options, this news is a beacon of hope. A therapy that can meaningfully extend life in this setting is a game-changer. It provides a desperately needed, effective treatment sequence after TKI failure. The positive OS data means more time—more birthdays, more holidays, and more moments with loved ones.
Beyond the immediate patient group, the success of HARMONi-3 has broader implications. It will likely influence clinical practice guidelines around the world. Clinicians may soon have a new, evidence-backed standard of care to offer. The global nature of the study, which included a significant cohort in China where this type of lung cancer is more prevalent, ensures the results are relevant to a diverse, worldwide population.
Furthermore, this success reinforces the importance of continued research and development in innovative drug design. As our understanding of cancer biology deepens, so does our ability to craft sophisticated therapies like ivonescimab. For authoritative information on cancer, the National Cancer Institute remains an excellent resource for patients and families.
Next Steps and Regulatory Outlook
With a successful Phase 3 trial in hand, Summit Therapeutics, along with its partner Akeso, is poised to move forward with regulatory submissions. The company has indicated plans to submit these results to regulatory authorities, including the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
The “statistically significant and clinically meaningful” OS benefit provides a strong foundation for these applications. While the regulatory review process is thorough and takes time, the clear positive outcome and the high unmet need in this patient population could lead to a priority review.
The oncology community will be eagerly awaiting the full data presentation at an upcoming medical meeting, which will provide deeper insights into the magnitude of the benefit, secondary endpoints like Progression-Free Survival (PFS), and the detailed safety profile. However, the top-line announcement is enough to confirm that we are witnessing the emergence of a new promising OS trend, one that brings renewed optimism and a powerful new weapon in the fight against lung cancer.
“`